-
API 예외처리-4 (ExceptionHandler)스프링 2023. 1. 28. 00:32
HandlerExceptionResolver 를 직접 사용하기는 복잡하다.
API 오류 응답의 경우 response 에 직접 데이터를 넣어야 해서 매우 불편하고 번거롭다.
ModelAndView 를 반환해야 하는 것도 API에는 잘 맞지 않는다. 스프링은 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 @ExceptionHandler 라는 매우 혁신적인 예외 처리 기능을 제공한다.
스프링은 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 를 기본으로 제공하고, 기본으로 제공하는 ExceptionResolver 중에 우선순위도 가장 높다.
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class) public ErrorResult illegalExHandler(IllegalArgumentException e) { log.error("ex", e); return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage()); } @GetMapping("/api2/members/{id}") public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) { if (id.equals("ex")) { throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자"); } if (id.equals("bad")) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값"); } if (id.equals("user-ex")) { throw new UserException("사용자 오류"); } return new MemberDto(id, "hello " + id); }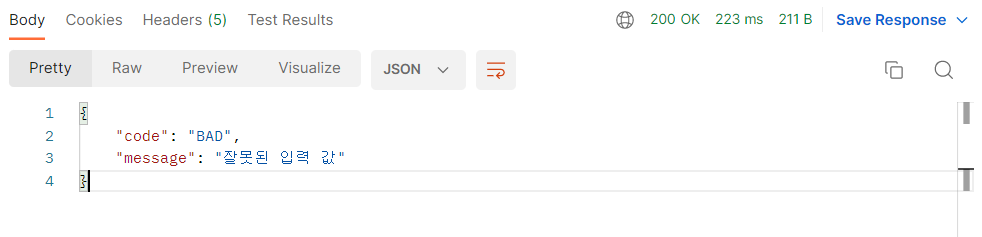
IllegalArgumentException이 발생하면 illegalExHandler가 호출된다.
바로 호출되는 것은 아니고 다음과 같은 과정을 거친다.

ExceptionResolver로 예외 해결 시도를 한다.(ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver가 실행된다.)
이때 @ExceptionHandler라는 어노테이션이 존재하면 이를 실행해준다.
이를 정상 흐름으로 바꾸어서 정상 흐름으로 return시킨다.
따라서 상태코드가 200이다...
따라서 상태 코드도 변경해야 한다.
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST) @ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class) public ErrorResult illegalExHandler(IllegalArgumentException e) { log.error("ex", e); return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage()); }다음과 같이 ResponseEntity도 사용이 가능하다.
@ExceptionHandler(UserException.class) public ResponseEntity<ErrorResult> userExHandler(UserException e) { log.error("ex",e); ErrorResult errorResult = new ErrorResult("USER-EX", e.getMessage()); return new ResponseEntity<>(errorResult, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST); }우선순위 스프링의 우선순위는 항상 자세한 것이 우선권을 가진다.
예를 들어서 부모, 자식 클래스가 있고 다음과 같이 예외가 처리된다.
@ExceptionHandler(부모예외.class) public String 부모예외처리()(부모예외 e) {} @ExceptionHandler(자식예외.class) public String 자식예외처리()(자식예외 e) {}@ExceptionHandler 에 지정한 부모 클래스는 자식 클래스까지 처리할 수 있다. 따라서 자식예외 가 발생하면 부모예외처리() , 자식예외처리() 둘다 호출 대상이 된다.
그런데 둘 중 더 자세한 것이 우선권을 가지므로 자식예외처리() 가 호출된다.
물론 부모예외 가 호출되면 부모예외처리() 만 호출 대상이 되므로 부모예외처리() 가 호출된다.
다음과 같이 다양한 예외를 한번에 처리할 수 있다.
@ExceptionHandler({AException.class, BException.class}) public String ex(Exception e) { log.info("exception e", e); }@ExceptionHandler 에 예외를 생략할 수 있다. 생략하면 메서드 파라미터의 예외가 지정된다.
@ExceptionHandler public ResponseEntity userExHandle(UserException e) {}728x90'스프링' 카테고리의 다른 글
@RequestBody vs @RequestParam (0) 2023.02.21 API 예외처리-5 (RestControllerAdvice) (0) 2023.01.28 API 예외처리-3 (0) 2023.01.27 API 예외처리-2 (0) 2023.01.27 API 예외처리-1 (0) 2023.01.26